Are you feeling a little lost after publishing your course in Storyline 360 and realizing that your high-quality WAV files have been transformed into MP3s? Don’t worry; you’re not alone. This micro-lesson is here to help clear things up and provide some much-needed guidance.
What is a WAV file?
WAV files are the real deal – they’re uncompressed, meaning they retain all the original audio data without any loss in quality. They are the gold standard for recording and editing audio. I always ask professional voice-over narrators to send me the narration files in WAV format (16-bit, 44 KHz PCM).
- 16-bit refers to the bit depth or the number of bits used to represent each audio sample. Higher bit depth means a greater dynamic range and a more accurate representation of the original recording.
- 44 KHz refers to the sample rate or the number of audio samples taken per second. The sample rate determines the frequency range of the audio that can be captured. 44 Khz means the audio is sampled 44,100 times per second.
- PCM stands for Pulse Code Modulation, a method for digitally representing analog audio signals. PCM is a common method for storing uncompressed audio data.
But let’s be real; there is one downside: they can be as large as a blue whale. Okay, maybe not that large, but you get the point – they take up a lot of space.
Now, if you’re using audio in your e-learning courses (and let’s be honest, who isn’t these days?), you want to keep your file size down to optimize the experience for your learners. So, what’s the solution? Well, MP3s, of course.
What is an MP3 file?
MP3 files are compressed audio files that use a lossy compression algorithm to reduce their file size while retaining most of the original audio quality.
Think of it like packing for a vacation. You only have limited space in your suitcase, so you must be selective about what you bring. You can’t bring your entire wardrobe, so you must choose the essential items you know you’ll wear. In the same way, MP3 files have limited space, so the lossy compression algorithm has to be selective about which sounds it keeps and which ones it discards. It only keeps the sounds essential to the audio’s overall quality and discards the rest to make the file size smaller.
What about bit rates? How do they affect file size?
Adjusting the bit rate in Storyline 360 is like choosing between quality and price when shopping. Like a higher quality product may come with a higher price tag, choosing a higher bit rate will result in better audio quality at the expense of a larger file size. On the other hand, opting for a lower bit rate is like choosing a cheaper product – it sacrifices some audio quality to achieve a smaller file size. It’s up to you to decide which is more important – a smaller file size or better audio quality – just like how you decide between quality and price when shopping.
Storyline 360! What did you do with my WAV files?
If you look closely after importing a WAV file into Storyline 360, you will notice it is automatically converted to an MP3 on the timeline and when you publish for distribution.
Why?
It helps balance file size with audio quality. Of course, you can adjust these settings and fine-tune them for your specific project.
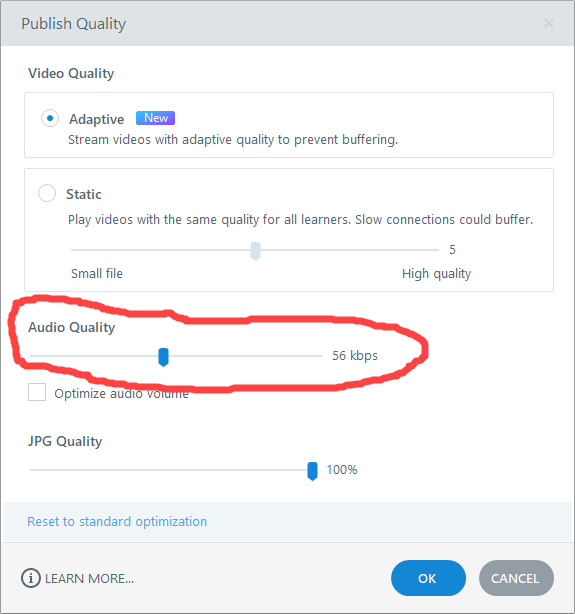
In Storyline 360 (v3.75.30269.0), the default setting results in the application using a 56 kbps bit rate, but the application provides a range from 16 kbps to 160 kbps. You can access this setting via Preview > Publish and then select Custom Optimization under the Quality Property setting.
If you need your file to reveal its true identity, you can export it back to the original WAV format. Right-click the audio file in the timeline and select Export Audio. Under the Save as type box, change it to Windows Audio File (.wav).
Can you really hear the difference?
The quality of the speakers you are using to listen to audio can significantly impact how noticeable the difference between a WAV and MP3 file is. High-quality speakers or headphones can provide a more accurate representation of the audio, making it easier to hear any subtle differences in quality between the two formats.
In contrast, lower-quality speakers may not be able to reproduce the nuances of the audio as accurately, making it more difficult to discern any differences between the two formats. However, it’s worth noting that even with high-quality speakers, the differences between a WAV and MP3 file may be subtle, and not everyone can hear them.
The more you know
Now that you’ve mastered this micro-lesson share your new knowledge with a friend, family member, or colleague. Who knows, you may even impress them with your newfound expertise! Keep learning and growing; I’ll see you in the next micro-lesson.

 Using a Storyline 360 Lightbox for a Glossary Slide
Using a Storyline 360 Lightbox for a Glossary Slide
Leave a Reply